Recently I’ve been retraining in Maya and giving myself extra alone time with the Arnold renderer from Solid Angle.
I decided to use this as not only an opportunity to find out how my Softimage lighting and rendering skills translate to Maya, but to show how basic compositing is something that every 3d artist should embrace if they don’t already.
One thing which has surprised me again and again is how little students and graduates of 3d courses are given a grounding in understanding what goes into their image and why it’s beneficial to use the compositing process as part of their workflow. Some students are even penalised for not showing their raw unenhanced render, having points deducted for daring to composite. To give a parallel, this to me is like a film photography student handing in negatives and no prints. The job is half done.
This won’t be a tutorial, more a pointer in the right direction for those who are starting out.
The example I use, a still life of a bowl of fruit, is a model from the very first lighting challenge hosted over at CGTalk. The files and others are downloadable at 3dRender. The model’s pretty old now so it’s not especially high detail but is still sufficient to show you what I intend to.
After a bit of setup in Maya and throwing on some pretty rough textures, here’s the beauty straight out of Arnold:
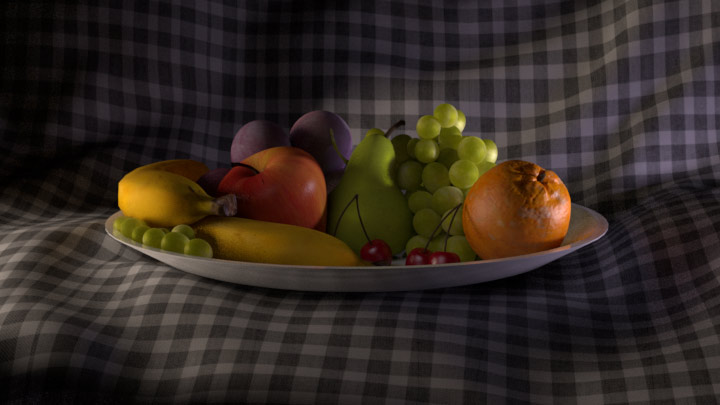

It’s lit with 3 lights; A cool exterior light, a warmer interior light, and a fill for the shadow in the middle. On their own, the images appear like this:

These images can be added together in any compositing software and they will give exactly the same result as the beauty above, to the extent that a pixel on the beauty will be exactly the same colour as when these three images are added together.
Each of these images is itself a composite image. Arnold, Mental Ray, Vray and other renderers consider many different material properties when returning the final colour for a particular pixel. Each property can be saved out as an image itself and added together to form the final image. In the case of the beauty itself, these are the images that I’ve rendered out of Arnold:
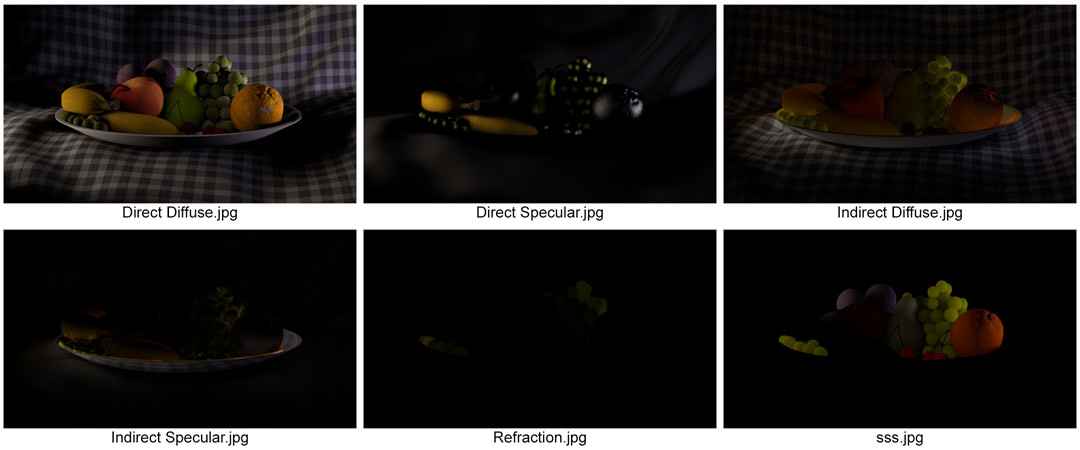
Again, added together, these form the same image as the beauty above perfectly.
(A side note here: A few component images are missing, including reflections, but were missed out of this contact sheet as they are entirely black. As none of the materials are reflective in the traditional sense, the reflection image is returned as black, whereas the direct specular contains highlights that mimic reflections. Arnold is peculiar in that it can consider reflections in 2 ways and transparency in 2 ways, depending on what is trying to be achieved.)So what am I getting at here?
Here’s the beauty again:

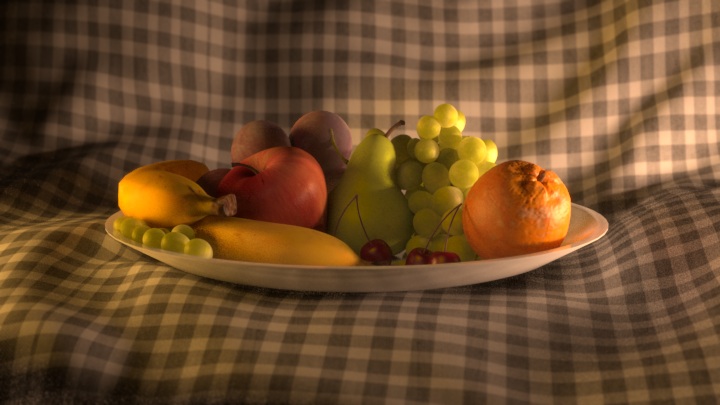
Now here is a warm, evening setup:

And finally, a night lighting setup:
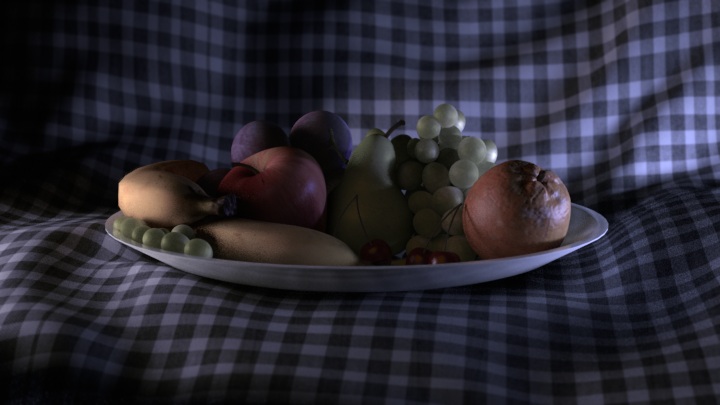

All three use the same component images, composited together in different ways: For example, tinting the lights, changing the intensity by blending the images with varying opacity, or even desaturating the key light to achieve a moonlit interior effect. On the night lighting I’ve changed the apple using a matte together with the specular & sss channels from the fill light. It was too bright and waxy. I could have re-rendered the 3d perhaps, but a tweak in Nuke was a lot more efficient.
The compositing process, even at this basic level, allows for flexibility from the get go. Where clients are concerned, flexibility is key. When passing work by a client it’s inevitable that changes will be requested and often they are something subtle that can be achieved in the composite. If you try to achieve that yourself using only 3d solutions, the render times will get long, especially when working on tv or film. Ordinarily I work alongside compositors and it’s up to them to do compositing tweaks whilst I work on a new shot or more substantial alterations to a current one.
Similarly, when first lighting a shot, working with many rendered channels, including additional ones of your own creation, is a rapid method of figuring out whether your setup is indeed heading in the right direction. Using the same component images for multiple looks is a time saver too.
One thing to bear in mind is once you know which channels are likely to be needed, it’s time to stop rendering the others as these can fill up hard drives quite nicely.
In short, stop tweaking your 3d scenes asap. Render out your initial lighting setup and see how much can be done in the comp. It isn’t cheating; It’s part of the process. It allows you to render the shot out, pass it on, and start a new one. Ultimately it will help your relationship with compositors who like to know what’s going into your image and what they need to add, plus [perhaps I shouldn’t say this, but here goes] it will make you more employable.

